What is hotel forecasting?
Hotel forecasting, also known as hotel demand forecasting, is a strategy that sees a hotel analyse historical data and trends to make predictions about future demand.
Once your hotel has an idea of demand, you can make tweaks to your room and service prices that help maximise revenue and occupancy. Hotel forecasting methods can also be used to inform everything from inventory levels – whether or not you offer more services or invest in building more rooms – to the booking channels and guests you target.
Hotel forecasting reports are built on a foundation of data. This can be internal data (from a hotel’s systems) and external data (competitor pricing and market trends). Modern forecasting tools can help to collect, organise and analyse all of this information.
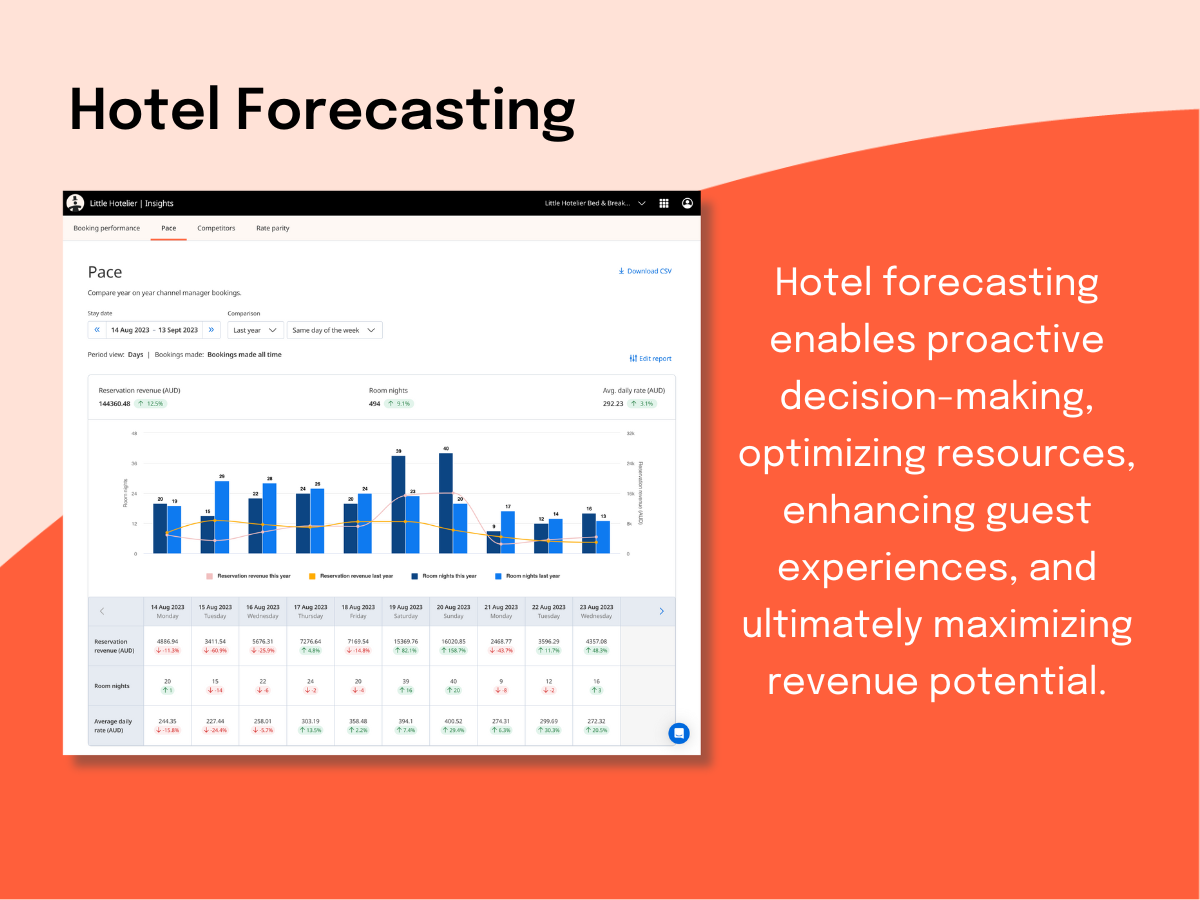
Price and promote your property better with Little Hotelier
Little Hotelier's Insights tool gives you more control, more support and more revenue. Access actionable rate insights and performance tracking
Learn moreWhy is hotel forecasting important?
The importance of forecasting in hotel industry businesses cannot be understated. Regularly generating and analysing forecasting reports can help you to:
- Develop strategies that boost your revenue and estimate your future profitability.
- Better predict and handle peak periods and slow periods.
- Ensure that you have the resources you need well ahead of time.
- Customise and optimise pricing strategies based on demand.
- Identify new markets and guest segments.
- Identify new KPIs that give you a deeper understanding of your hotel’s performance.
In short, hotel forecasting gives you a glimpse into the future, which enables you to improve your hotel strategies and performance right now.
Factors that affect hotel demand forecasting
Hotel forecasting means different things to different hotel businesses. Small, independent hotels might form quite basic forecasts. Multinational chains, meanwhile, can dedicate entire teams to developing intricate forecasts that consider a wealth of factors.
With that in mind, the factors that affect hotel demand forecasting will vary, but a few of the most common include:
- Booking data: Historical booking data for both your hotel and competitor hotels, including how bookings vary through peak, shoulder and low seasons.
- Pricing data: Hotel and competitor pricing data, including how it varies throughout the year.
- Cancellation data: How types of guests and times of year affect cancellation and no-show rates.
- Reputation data: Online ratings and reviews, and how they compare to your main competitors.
- Outlier factors: How special events and unusual occurrences have historically affected demand (e.g. bad weather, surprise events or event cancellations).
Hotel forecasting methods and process
Demand forecasting in hotel industry businesses can take a few different forms. Three of the most common hotel forecasting methods include:
- Revenue management forecasting: Used to predict future demand. These forecasts allow you to implement revenue optimisation strategies based on anticipated occupancy.
- Operational forecasting: Used to predict the resources required for the smooth operation of your hotel, which helps you to arrange adequate staff levels and order the materials you need.
- Financial forecasting: Used to predict future financial results. These forecasts help hotel leaders establish and work towards realistic financial goals.
These forecasts are designed to answer different questions, so they will use different data and different methods along the way. Nevertheless, the following process can generally be applied to all three:
Step 1: Collect data
Identify and collect the data that will inform your forecast. Put a focus on your own historical booking and pricing data, supplemented by data relating to competitors and market trends.
Step 2: Identify patterns
Use a forecasting tool to find patterns. Work to identify opportunities and understand why issues occur, such as the reason behind cancellations and no-shows.
Step 3: Analyse demand
Generate booking demand insights around KPIs like ADR, RevPAR, lead time and average length of stay. Understand exactly when peak and low periods occur throughout the year.
Step 4: Take action
Informed by your forecast, develop strategies that optimise revenue during peak periods and generate revenue during low season. Customise your strategies in line with the needs and demands of different market segments.
Step 5: Regularly review
Review your forecast regularly, making adjustments as the market evolves. Adjust your goals as new information comes to light.
How hotel forecasting technology can help small hotels
There was a time, not so long ago when only the biggest hotel chains capitalised on demand forecasting. But the development of clever and affordable tools now means that any hotel, even small, independent operations, can see into the future.
In this way, hotel forecasting technology helps to level the playing field for smaller accommodation providers. If an independent operator is willing to invest a little bit of money, time and effort, they can gain access to high-level insights that help them enter new markets, attract new guests, and maximise their bookings and revenue.
At its best, hotel demand forecasting can predict how much each type of guest will be willing to pay at any moment in time. It helps you to be more flexible and agile with your room rates, while removing the stress, pressure and guesswork of setting prices and developing growth strategies.
By Dean Elphick
Dean is the Senior Content Marketing Specialist of Little Hotelier, the all-in-one software solution purpose-built to make the lives of small accommodation providers easier. Dean has made writing and creating content his passion for the entirety of his professional life, which includes more than six years at Little Hotelier. Through content, Dean aims to provide education, inspiration, assistance, and, ultimately, value for small accommodation businesses looking to improve the way they run their operations (and live their life).
Table of contents
“Our lives are made a little easier because of Little Hotelier. It helps increase revenue by utilising a variety of distribution methods.”
Owner, Silan Residence









Mick Comerford,
General Manager
The Mercantile Hotel